竞赛内容:https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wGhjB8iqROP4Ovs78SrmGrZcxDbrATPX9CFyKd7pTxo/edit
Branch Predictor汇总:https://www.cnblogs.com/arthurzyc/p/16895277.html
汇总:https://blog.csdn.net/edonlii/article/details/8754724
例子解释
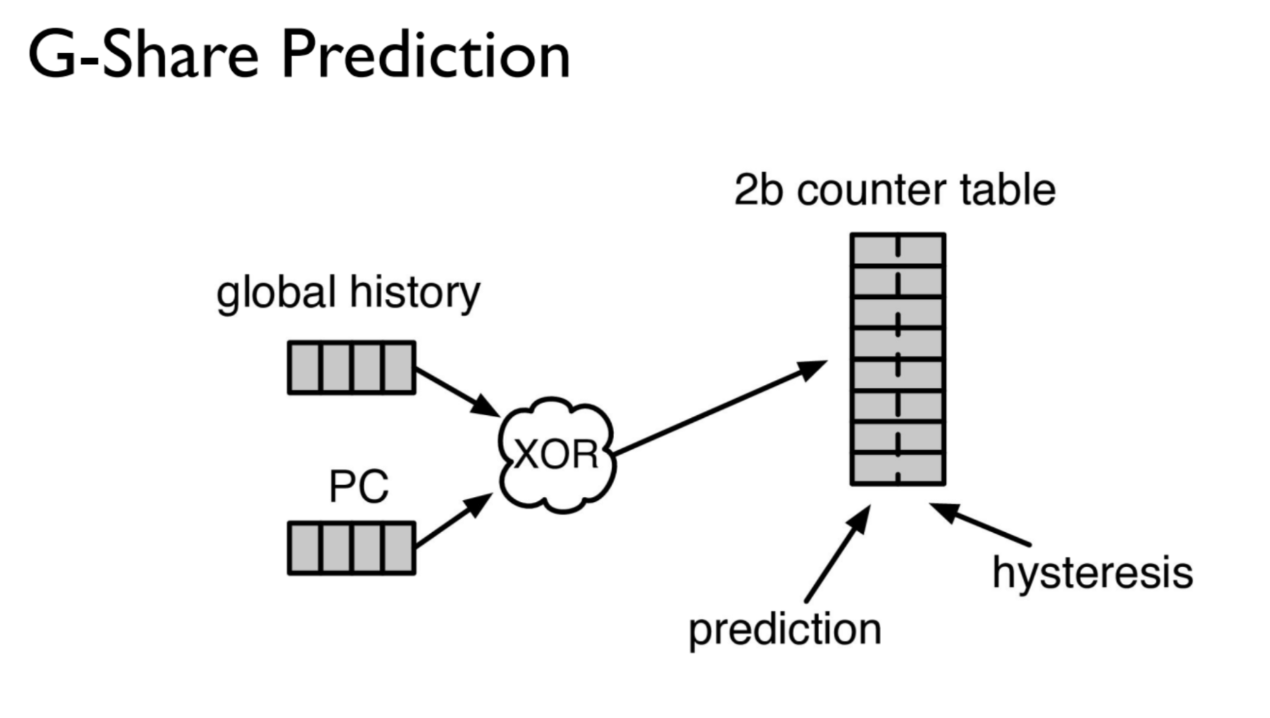
例子用的是G-share predictior,就是将Global History和PC进行XOR。这么做是因为PC太长了,我们只会会取PC的里面的几位,但有一个问题,有些instructions的PC的那几位是一样的,所以如果存进prediction table里就会影响结果。所以我们加入了Global History和PC进行XOR,XOR后得到的数据本身并没有意义,并不能说明任何事情(如这个instruction有没有发生过),它就只是作为prediction table的index,它的value(00 strongly not take,01,10,11)才是告诉predictor自己有没有发生过的。用XOR:原因一是适合被解耦,可以释放出原来的PC值;原因二是处理一下PC从而区别出更多PC,得到的index数量 > types of PC的那几位。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 class my_update : public branch_update {public : unsigned int index; }; class my_predictor : public branch_predictor {public :#define HISTORY_LENGTH 15 #define TABLE_BITS 15 my_update u; branch_info bi; unsigned int history; unsigned char tab[1 <<TABLE_BITS]; my_predictor (void ) : history (0 ) { memset (tab, 0 , sizeof (tab)); } branch_update *predict (branch_info & b) { bi = b; if (b.br_flags & BR_CONDITIONAL) { u.index = (history << (TABLE_BITS - HISTORY_LENGTH)) ^ (b.address & ((1 <<TABLE_BITS)-1 )); u.direction_prediction (tab[u.index] >> 1 ); } else { u.direction_prediction (true ); } u.target_prediction (0 ); return &u; } void update (branch_update *u, bool taken, unsigned int target) if (bi.br_flags & BR_CONDITIONAL) { unsigned char *c = &tab[((my_update*)u)->index]; if (taken) { if (*c < 3 ) (*c)++; } else { if (*c > 0 ) (*c)--; } history <<= 1 ; history |= taken; history &= (1 <<HISTORY_LENGTH)-1 ; } } };
G-share结果数据展示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 traces/164.gzip/gzip.trace.bz2 12.473 traces/175.vpr/vpr.trace.bz2 13.415 traces/176.gcc/gcc.trace.bz2 11.254 traces/181.mcf/mcf.trace.bz2 15.837 traces/186.crafty/crafty.trace.bz2 5.837 traces/197.parser/parser.trace.bz2 10.008 traces/201.compress/compress.trace.bz2 7.831 traces/202.jess/jess.trace.bz2 1.562 traces/205.raytrace/raytrace.trace.bz2 2.756 traces/209.db/db.trace.bz2 3.909 traces/213.javac/javac.trace.bz2 2.267 traces/222.mpegaudio/mpegaudio.trace.bz2 2.188 traces/227.mtrt/mtrt.trace.bz2 2.657 traces/228.jack/jack.trace.bz2 3.033 traces/252.eon/eon.trace.bz2 1.807 traces/253.perlbmk/perlbmk.trace.bz2 2.554 traces/254.gap/gap.trace.bz2 3.926 traces/255.vortex/vortex.trace.bz2 1.222 traces/256.bzip2/bzip2.trace.bz2 0.094 traces/300.twolf/twolf.trace.bz2 21.489 average MPKI: 6.305
不同程序的分支预测失误率(Misses Per Kilo Instructions, MPKI),这是衡量分支预测器性能的一个关键指标。这些数据显示了各种不同类型的程序在G-Share预测器下的表现,其中一些程序的MPKI较高,表明分支预测失误较频繁,而有些程序的MPKI较低,预测相对较准确。
从数据来看,程序如 twolf 和 mcf 显示出非常高的 MPKI,可能是因为这些程序的分支模式特别复杂或包含大量的循环和条件分支,而G-Share预测器可能无法有效处理这种复杂性。而像 bzip2 这样的程序显示出极低的 MPKI,表明其分支模式相对简单或者与G-Share预测器的预测模式非常匹配。
对于G-Share预测器而言,其性能限制:
索引冲突(Alias Problem):
XOR操作用于生成索引可能会导致不同的分支历史和PC地址组合产生相同的索引结果。这种Alias问题可能导致预测错误,因为不相关的分支使用了相同的预测表条目,从而互相干扰。
全局历史长度限制:
G-Share使用固定长度的全局历史来生成索引,这可能不足以捕捉长期依赖或复杂分支模式,尤其是在大型或复杂的程序中。
预测表大小限制:
预测表的大小直接影响能够跟踪的分支上下文数量。表大小有限可能会导致更多的冲突和替换,尤其是在那些具有广泛分支行为的大型应用程序中。
统一预测策略的局限性:
G-Share预测器采用统一的预测策略来处理所有分支,不考虑分支类型的多样性和程序上下文的复杂性。
我的想法,为了改善 G-Share 预测器的性能,暂时考虑以下策略:
采用混合或锦标赛预测器(Hybrid or Tournament Predictor) :结合使用不同类型的预测器,如局部history predictor和G-Share predictor,然后用selector选择表现最佳的预测器。增加历史长度和表大小 :根据资源允许的情况,适当增加全局历史的长度和预测表的大小,以减少冲突并改善预测准确性。改进XOR散列函数 :尝试使用更复杂的散列函数代替简单的XOR,以降低冲突率。引入路径感知预测 :考虑路径信息或程序执行上下文来增强预测器的决策能力。
当我只更改History Table Length时,将 HISTORY_LENGTH 从15增加到16时,增加了分支预测器使用的历史信息长度。这种改变理论上应该提供更多的历史数据来帮助预测器做出更准确的预测。然而,实际上MPKI(每千条指令失误预测数,Misses Per Kilo Instruction)增加了,这表明准确性实际上变差了。原因:
1. History Info的过度拟合
扩大 HISTORY_LENGTH可能导致预测器过度拟合特定的history,特别是在history不稳定或者过于复杂时。这可能导致预测器在面对不遵循已经见过的history的新情况时表现不佳。就像人如果只根据过去的经验做决定,有时候可能会错过新情况的正确处理方法。predictor也一样,如果history info太长,可能就难以灵活应对那些不太符合以往模式的新情况。
2. 表项碰撞(Table Entry Collisions)
如果 TABLE_BITS 保持不变而只增加 HISTORY_LENGTH,这可能导致更多的索引碰撞。由于现在有更多的history info被压缩到同样大小的index table中,不同的history可能映射到相同的表项上,增加了冲突的可能性,从而降低预测的准确性。就像预测器有一个用来存储history的table,如果HISTORY_LENGTH增加,不同的history info可能会被压缩到table的同一个位置。这就像多个人要抢同一个座位,最终可能导致混乱,predictor也难以准确预测。
3. 表容量不足
与上面的点相关,增加HISTORY_LENGTH而不相应增加predictor的大小(由 TABLE_BITS 决定),可能导致predictor的有效容量不足以覆盖更多的history组合。这会限制预测器学习和适应新模式的能力。增加HISTORY_LENGTH而不扩大predictor table的大小,就好比文件越来越多但文件柜的大小不变,最终文件柜装不下,找文件时也更费劲。
我的方法
由于懒,我用的是相对简单的优化方法。关键词是 Local Branch Predictor,Bimodal Predictor,G Share。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 class my_update : public branch_update {public : unsigned int index; }; class my_predictor : public branch_predictor{public :#define BHR_num 22 #define PT_BITS 22 #define BMODAL_BITS 15 unsigned char BimodalTable[1 << BMODAL_BITS]; my_update u; branch_info bi; unsigned int history; unsigned int BHRTable[BHR_num]; unsigned char PTable[1 <<PT_BITS]; my_predictor (void ) : history (0 ){ for (int i = 0 ; i < BHR_num; i++) { BHRTable[i] = 0 ; } memset (PTable, 0 , sizeof (PTable)); memset (BimodalTable, 4 , sizeof (BimodalTable)); } branch_update *predict (branch_info &b) { bi = b; unsigned int bimodal_index = b.address & ((1 << BMODAL_BITS) - 1 ); bool bimodal_prediction = (BimodalTable[bimodal_index] >> 1 ) & 1 ; if (b.br_flags & BR_CONDITIONAL) { u.index = BHRTable[history ^ (b.address & ((1 <<PT_BITS)-1 ))]; bool local_prediction = (PTable[u.index] >> 1 ) & 1 ; if (PTable[u.index] == 3 || PTable[u.index] == 4 ) { u.direction_prediction (bimodal_prediction); } else { u.direction_prediction (local_prediction); } } else { u.direction_prediction (true ); } u.target_prediction (0 ); return &u; } void update (branch_update *u, bool taken, unsigned int target, branch_info &b) if (bi.br_flags & BR_CONDITIONAL) { unsigned char *c = &PTable[((my_update*)u)->index]; if (taken) { if (*c < 7 ) (*c)++; } else { if (*c > 0 ) (*c)--; } unsigned int bimodal_index = b.address & ((1 << BMODAL_BITS) - 1 ); if (taken) { if (BimodalTable[bimodal_index] < 7 ) BimodalTable[bimodal_index]++; } else { if (BimodalTable[bimodal_index] > 0 ) BimodalTable[bimodal_index]--; } BHRTable[history ^ (b.address & ((1 <<PT_BITS)-1 ))] <<= 1 ; BHRTable[history ^ (b.address & ((1 <<PT_BITS)-1 ))] |= taken; BHRTable[history ^ (b.address & ((1 <<PT_BITS)-1 ))] &= (1 <<14 )-1 ; history <<= 1 ; history |= taken; history &= (1 <<BHR_num)-1 ; } } };
最后达到的MPKI是5.020。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 traces/164.gzip/gzip.trace.bz2 12.699 traces/175.vpr/vpr.trace.bz2 12.147 traces/176.gcc/gcc.trace.bz2 7.318 traces/181.mcf/mcf.trace.bz2 14.578 traces/186.crafty/crafty.trace.bz2 3.944 traces/197.parser/parser.trace.bz2 8.373 traces/201.compress/compress.trace.bz2 7.429 traces/202.jess/jess.trace.bz2 0.980 traces/205.raytrace/raytrace.trace.bz2 1.206 traces/209.db/db.trace.bz2 3.559 traces/213.javac/javac.trace.bz2 1.712 traces/222.mpegaudio/mpegaudio.trace.bz2 1.670 traces/227.mtrt/mtrt.trace.bz2 1.325 traces/228.jack/jack.trace.bz2 1.626 traces/252.eon/eon.trace.bz2 0.898 traces/253.perlbmk/perlbmk.trace.bz2 1.178 traces/254.gap/gap.trace.bz2 2.423 traces/255.vortex/vortex.trace.bz2 0.490 traces/256.bzip2/bzip2.trace.bz2 0.091 traces/300.twolf/twolf.trace.bz2 16.768 average MPKI: 5.020
首先,我定义了Branch History Register Table,这是一列数组,每行是int大小的BHR(Branch History Register)。BHR是用来作为PT(Pattern Table)的index的。这样做的目的是相当于直接对每个Branch instruction单独进行history统计,相比之下例子中的G-Share是只用一串history数据对所有Branch进行统一操作。然后我也往里面增加了G-Share的思路,就是再用一串history数据和PC进行XOR,特异化PC,然后作为BHRT存history用每个的index。这里的大体优化就差不多了。
进一步小优化,我用了Bimodal的思路。我设置的是3-bit count table(111 stands for Strongly Taken),也就是计数到7。但会有问题,比如011(3)和100(4)时,我们的判断并没有那么强力。所以加入Bimodal Predictor,这个predictor的table就是在记录index时完全不考虑history,直接把PC存进去。所以我们做一个判断,当带着History的predictor预测出这种边缘值时,我们该用Bimodal Predictor。
双模态表 (BimodalTable)仅使用程序计数器(PC)的低位部分来索引。这种方法使得预测更加依赖于指令的位置而非其执行历史。双模态表更多地反映了特定程序地址的分支行为的统计趋势。局部预测表 (PTable)结合了全局历史记录(history)和PC的特定位,通常是通过异或操作来生成索引。这样做可以捕捉到与过去的分支决策相关联的模式,使预测能够适应程序行为的变化。
更优秀的方法应该用TAMG或者一些机器学习的方法。贴一个TAMG的实现方法,有兴趣可以看着论文去实现:https://github.com/Satjpatel/Branch-Predictor-Project/blob/fb34a61660f788c0339b68218e5c790d43d77e0e/Newr Final Infrastructure/cbp2-infrastructure-v3/src/my_predictor.h#L37